
- Installing linux on a mac how to#
- Installing linux on a mac mac os x#
- Installing linux on a mac mac os#
- Installing linux on a mac install#
For this reason I didn’t use the iMac often. After I tried using the iMac and installing apps on it I found out that few apps supported Snow Leopard. The highest MacOS it can support is 10.6 or Snow Leopard. Nvidia GeForce 7300 GT video card 128 MB VRAM.24-Inch screen TFT Active Matrix LCD (1921x1200 native) display.For this article I used an iMac 6.1 from late 2006. There are many types of Apple Mac systems available.
Installing linux on a mac install#
For this reason someone may want to install Linux on a Mac.

Installing linux on a mac mac os#
If you installed Linux as the only operating system and replaced Mac OS X, you’ll need to reinstall OS X on your Mac if you want to leave Linux behind.Many people may like the look and feel of Linux over other Desktop Operating Systems (OS).
Installing linux on a mac mac os x#
After the partitions are deleted, you can enlarge your Mac OS X partition afterwards from the Disk Utility in OS X to reclaim the space used for Linux. You can also boot from your Linux USB media and use the GParted partition manager to remove these partitions. Boot into OS X, open the Disk Utility, and delete your Linux partitions. If you decide you no longer want to dual boot Linux on your Mac, you can remove Linux fairly easily.
Installing linux on a mac how to#
RELATED: How to Wipe Your Mac and Reinstall macOS from Scratch Other users have probably dealt with the same problems before you, and they’ve probably written guides to making everything work. If something doesn’t work, you may have to perform some Google searches with the model and year of your Mac as well as the name and version of the Linux distribution you’re using. This depends on the version of Linux you use, how recent it is, and what Mac hardware you’re using. Whenever you boot your computer, you’ll have the ability to choose between Mac OS X and Linux on the rEFInd boot manager screen.ĭepending on your Mac, some hardware components may not work perfectly on Linux. The installation process should otherwise be normal. Be sure to select the “Install Ubuntu alongside Mac OS X” option instead of overwriting your Mac OS X system with Ubuntu. On Ubuntu, launch the Install Ubuntu application from the desktop and install Ubuntu as you normally would.
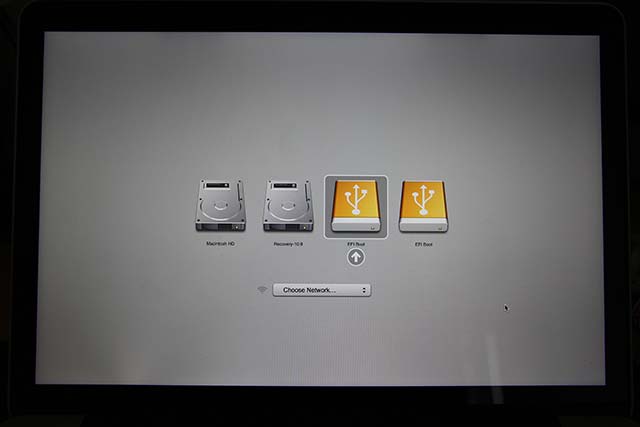
Launch your Linux distribution’s installer and go through the installation process. Select the USB or disc drive containing the Linux system and boot it on your Mac. Restart your computer and rEFInd will appear. Burn the ISO to disc or follow Ubuntu’s official instructions to create a bootable USB drive from the ISO file. For example, if you’re using Ubuntu, you’ll need to download an Ubuntu ISO file - download the “64-bit Mac” version. You’ll need Linux installation media to continue. Drag and drop the handle on the partition volume or enter a final size for the partition and click Partition to partition it.ĭon’t create a new partition after shrinking your current partition - just leave the space empty for now. Ubuntu’s system requirements say it requires at least 5 GB of space, but something like 20 GB is much more reasonable. How much space you want for Linux is up to you. Shrink the current Mac OS X partition to make space for your Linux system. RELATED: Beginner Geek: Hard Disk Partitions Explained Select your Mac’s hard drive in the list on the left and select Partition on the right. From within Mac OS X, press Command + Space, type Disk Utility, and press Enter to open the Disk Utility.
/dual-boot-linux-and-mac-os-4125733-e14f9fd4e70f4577a4ff4fb7a2ac9e56.jpg)
You’ll now need to resize your Mac OS X system partition to make room for your Linux distribution of choice. You should see the rEFInd boot manager screen. Shut down your Mac - a full shut down, not a restart - and boot it back up again.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
